The impact of hydrogen on the labor market and business
Did you know that the Ohio River Valley is considered a prime location for a hydrogen and carbon capture and storage (CCS) market center?
With the Labor Energy Partnership at the helm, there’s a strong, unified push to accelerate the region’s clean energy economy. This leadership is preserving jobs and economic performance and significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It demonstrates how technology and innovation can be leveraged to save jobs, strengthen communities, and protect the planet, all while prioritizing workers’ rights and quality employment opportunities.
The hydrogen workforce 2024 is seeing significant growth and development, driven by initiatives across various sectors to foster the clean energy transition. Notable developments include the establishment of hydrogen hubs and targeted education and training programs to prepare the workforce for emerging opportunities in the hydrogen sector.
Establishing hydrogen hubs, like the Mid-Atlantic Clean Hydrogen Hub (MACH2), is set to be a game-changer, creating many jobs across the United States. These hubs are about integrating hydrogen production, consumption, and distribution and fostering workforce development in collaboration with academic institutions and industry partners. For instance, the University of Delaware is leading in workforce development for MACH2, working alongside other universities to develop academic programs that cater to the clean energy sector’s needs.
Moreover, the U.S. Department of Energy has allocated funding to support training for the next-generation hydrogen workforce. This includes grants for projects that advance clean hydrogen technologies and educate science and engineering students, particularly at Minority-Serving Institutions. These projects aim to reduce costs in the hydrogen production and usage sectors while exposing students to groundbreaking research and practical experiences in the field.
About hydrogen
Hydrogen, a universal and clean energy carrier, is at the forefront of global efforts to revolutionize energy production, storage, and usage.
This attention is driven by its potential as a clean alternative to fossil fuels, offering a promising path to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy future.
Pros
Advances in hydrogen production technologies, particularly carbon capture and storage (CCS), hold significant potential to reduce carbon emissions and tackle the urgent environmental challenges of climate change.
CCS technology, for instance, is designed to capture carbon dioxide emissions at their sources, such as power plants and industrial sites, thereby mitigating greenhouse gases’ impact.
Cons
However, the transition to hydrogen energy and the integration of CCS technology are not without challenges. These include:
- High production and operating costs
- The energy-intensive nature of current hydrogen production processes
- Extensive infrastructure development is required to support widespread adoption.
Despite these obstacles, the growing focus on hydrogen as a critical component of future energy systems highlights its potential role in contributing to global environmental sustainability goals. As research and technology advances, hydrogen power becomes vital in transitioning to a cleaner and more sustainable energy environment.
The hydrogen boom and its impact on the global workforce
The world is experiencing an unparalleled increase in hydrogen projects, with an astounding 1,418 initiatives announced globally. Among these, 1,011 projects are set to undergo complete or partial deployment by 2030, reflecting a significant change towards cleaner and more efficient energy sources.
Investors demonstrate their unwavering confidence in hydrogen, as evidenced by the substantial USD 570 billion in direct investments announced for hydrogen projects through 2030. This represents a significant 30% increase, with USD 39 billion already reaching the Final Investment Decision (FID) milestone, a clear indication of the firm commitment to the hydrogen revolution.
The potential of clean hydrogen is further underscored by the ambitious goals set for hydrogen supply. A staggering 45 million metric tons per year (Mt p. a.) of clean hydrogen supply was announced for 2030. What makes this commitment even more compelling is its environmental impact, with 70% of the announced supply being renewable and the remaining 30% designated as low carbon, a significant step towards global efforts to combat climate change.
As we reflect on the current state of hydrogen adoption, it’s noteworthy that 2022 marked a crucial moment with 1,020 hydrogen refueling stations in operation worldwide. Nations like Italy, Germany, and Spain led the charge, signaling a global shift towards embracing hydrogen as a viable energy alternative.
Source: ING Research
The impact of this hydrogen boom extends beyond infrastructure and environmental benefits — it’s set to reshape the global workforce.
According to insights from the European Commission, the European Hydrogen Value Chain is projected to generate approximately 1 million highly skilled jobs by 2030 and an astonishing 5.4 million by 2050. This underscores hydrogen’s economic potential and highlights its role in fostering a workforce revolution that aligns with the demands of a sustainable future.
To provide a clearer understanding of the workforce implications arising from the surge in the hydrogen trend, let’s explore the specific case of hydrogen’s influence on the chemical and pharmaceutical industry job market. The insights presented below are derived from an analysis of over 450,000 global job advertisements conducted by HRForecast in cooperation with Bundesarbeitgeberverband Chemie (BAVC) and Industriegewerkschaft IGBCE.
Examples of hydrogen in the chemical & pharmaceutical industry
Examples of hydrogen in the chemical & pharmaceutical industry
The push for green chemistry and the integration of hydrogen illustrates a commitment to care for the environment while maintaining profitability. The push for blue and green hydrogen as alternatives to carbon-intensive gray hydrogen reflects a broader shift toward sustainable and circular economy practices in the chemical sector.
The pharmaceutical industry is using green chemistry to innovate while reducing environmental impact. Adopting principles of green chemistry, such as the atom economy principle, is helping pharmaceutical companies such as Merck and Amgen develop more efficient and less wasteful production methods. For example, Merck’s development of molnupiravir for the treatment of COVID-19 significantly reduced solvent waste and increased yields, demonstrating the practical benefits of integrating environmental chemistry into pharmaceutical research and development.
Hydrogen’s versatility extends beyond chemical feedstocks, finding applications in various industrial sectors. Because of its low density and high thermal conductivity, it serves as a coolant in large electrical generators, acts as a tracer gas for leak detection, and plays a crucial role in producing methanol by converting carbon dioxide. Furthermore, it contributes to hydrogen peroxide production using more environmentally friendly methods. These diverse applications underscore hydrogen’s critical role in enhancing industrial processes, promoting energy efficiency, and fostering environmental sustainability.
Hydrogen trend analysis
The slight decline in job demand indicates that the primary demand is in industries other than chemical and pharmaceutical companies. Positions important to this trend, such as maintenance and manufacturing, require skills such as catalysis, CAD software, and corrosion control — roles typical in other industries (e.g., automotive).
Let’s take a closer look at each functional area, exploring how the hydrogen trend affects different aspects of business operations:
Administration (0.37%)
Although administration shows a moderate impact, this suggests the need for managerial and logistical support to accommodate the changes associated with hydrogen integration. This may include:
Regulatory compliance. Admin teams may need to comply with new hydrogen production, storage, and distribution regulations. The responsibilities may include documentation, reporting, and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Organizational changes. As companies integrate hydrogen technologies, administrative roles may be involved in organizational changes, including creating new departments or teams focused on hydrogen-related initiatives.
HR (0.20%)
Human resources may experience relatively little impact, indicating that the hydrogen trend may not significantly change HR practices. However, HR professionals need to support the hiring and training of personnel with specific hydrogen technology skills:
Skill development. Although the impact on HR is modest, HR professionals may need to facilitate skills development programs. This includes identifying and nurturing talent with experience in hydrogen technologies and processes.
Recruitment strategies. HR teams can adapt recruitment strategies to attract people with experience in sustainable technology and the emerging hydrogen sector.
IT (0.22%)
IT departments can implement and manage software solutions related to hydrogen production, storage, distribution, and cybersecurity of hydrogen infrastructure.
Software implementation. IT departments may implement and manage software solutions for hydrogen-related processes. This could include data analytics, control systems, and cybersecurity measures to safeguard hydrogen infrastructure.
Integration with existing systems. IT professionals may need to integrate new hydrogen technologies with existing IT systems, ensuring seamless communication and data exchange.
Maintenance (1.08%)
There is a critical need for skilled personnel to ensure the maintenance and reliability of hydrogen-related infrastructure, including hydrogen production facilities, distribution networks, and related equipment.
Equipment upkeep. Maintenance teams play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and safety of hydrogen infrastructure by conducting regular inspections, performing preventive maintenance, and swiftly responding to operational issues.
Training programs. Given the specialized nature of hydrogen-related equipment, maintenance personnel can undergo special training programs to enhance their skills in handling and servicing hydrogen technology.
Marketing (0.30%)
Marketing has a moderate effect, suggesting that companies may need to adjust their marketing strategies to emphasize their involvement in hydrogen-related projects. The message of hydrogen’s environmental benefits and sustainability aspects can become more prominent in marketing campaigns.
Sustainability messaging. Marketing efforts can highlight hydrogen’s environmental benefits, positioning the company as a leader in green practices.
Educating stakeholders. Marketers could play a role in educating customers and stakeholders about the benefits of hydrogen solutions, promoting a positive perception of the company’s commitment to sustainability.
Procurement (0.55%)
Procurement sees a moderate impact, indicating that there may be changes in sourcing materials and technologies related to hydrogen production.
Supplier relationships. Procurement teams can establish and strengthen relationships with suppliers that offer hydrogen-related components, such as electrolyzes, storage tanks, and specialty materials.
Sourcing sustainability. The focus may be on finding materials with a low environmental impact that aligns with the sustainable development goals associated with the introduction of hydrogen.
Production (1.09%)
Manufacturing will be significantly impacted, highlighting hydrogen’s transformative impact on manufacturing processes. The integration of hydrogen into production processes, especially in industries such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals, requires adjustments to ensure efficiency and sustainability.
Process optimization. Production teams will likely need to optimize manufacturing processes to incorporate hydrogen, ensuring efficiency and reducing carbon emissions.
Integration of hydrogen technologies. Companies may invest in upgrading production facilities to accommodate hydrogen-related technologies, requiring collaboration between production and R&D teams.
R&D (1.05%)
Research and development has a significant impact, highlighting the critical role of research and development teams in advancing hydrogen-related processes and applications. This underlines the increased emphasis on innovation and the development of new hydrogen-related technologies.
Innovation in hydrogen technologies. Groups of researchers and developers will be at the forefront of innovation, developing new technologies and methodologies related to hydrogen production, storage, and use.
Collaboration with production. R&D specialists can work closely with production teams to integrate new technologies into production processes.
Sales (0.27%)
Sales show a relatively modest impact, suggesting that while the hydrogen trend may influence sales strategies, it may not be the primary driver for sales teams. However, companies may need to emphasize the benefits of hydrogen solutions to potential customers.
Highlighting benefits. Sales departments should highlight the benefits of hydrogen solutions to potential customers, emphasizing how these technologies meet sustainability and efficiency goals.
Adapting sales strategies. Sales strategies can be tailored to demonstrate the competitive advantages of the company’s hydrogen-related products and services.
Supply chain (0.85%)
The supply chain will be significantly affected, indicating the need for optimization to ensure the supply and distribution of hydrogen-related materials and products.
Optimizing logistics. The supply chain should be optimized to ensure efficient supply and distribution of hydrogen-related materials and products.
Sustainability in sourcing. Supply chain professionals can prioritize suppliers with green practices, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain.
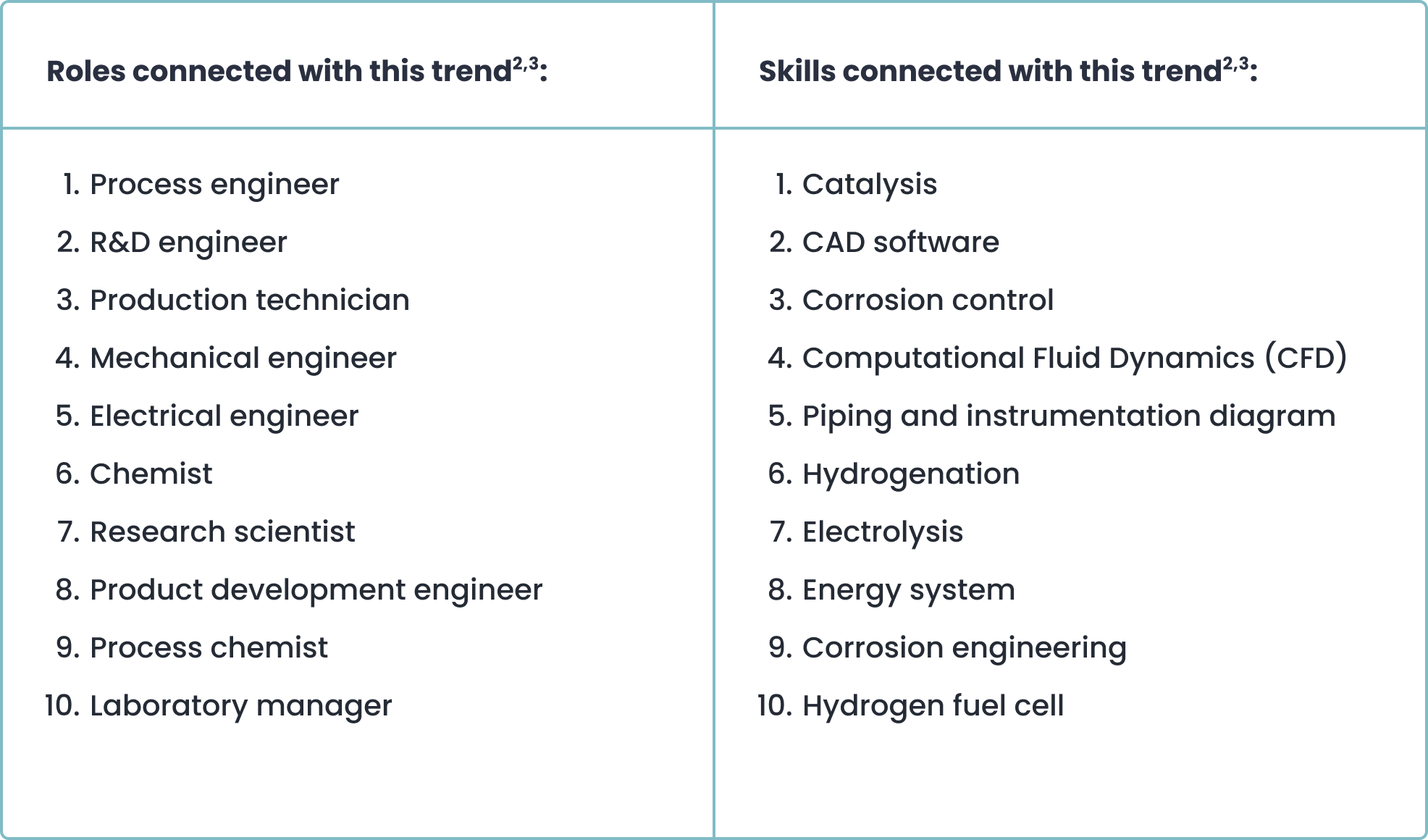
Roles and skills connected with the hydrogen trends
Interest in hydrogen technology is growing, as seen from the listed professional roles and required skills.
Positions such as process, mechanical, and electrical engineers involve complex participation in the design, operation, and maintenance of hydrogen production and utilization systems.
In addition, R&D engineers, chemists, and research scientists point to significant investments in scientific discovery and innovation to optimize hydrogen processes.
Positions such as laboratory manager and production technician require close supervision and execution of hydrogen-related operations.
Regarding skills
The relevant skills underline the technical breadth required in the hydrogen sector. Mastery in catalysis and electrolysis focuses on the chemical production of hydrogen, while proficiency in CAD software is essential for designing these complex systems.
Knowledge of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and energy systems indicates the need to model and optimize hydrogen flows and related energy transformations.
Skills in corrosion control and familiarity with hydrogen fuel cells are also critical, highlighting the challenges of material durability and the push for sustainable hydrogen energy solutions.
Wrapping up
The global growth of hydrogen projects shows strong confidence in hydrogen’s potential as a clean energy vector, highlighted by significant investment and ambitious targets for clean hydrogen supply. Despite challenges such as high operating costs and the need for extensive infrastructure, the push for hydrogen power is a testament to its key role in achieving a sustainable and low-carbon future. It promises a transformative impact on the global workforce, helping to create millions of high-skilled jobs and ushering in a new era of sustainable industrial practices in sectors ranging from chemicals and pharmaceuticals to energy generation and beyond.
Stay up to date with our newsletter
Every month, we’ll send you a curated newsletter with our updates and the latest industry news.



























 info@hrforecast.de
info@hrforecast.de
 +49 89 215384810
+49 89 215384810






