Influence of Generative AI on productivity and why it’s time to upskill
Table of contents
- What do people think about Generative AI?
- What is Generative AI really?
- Generative AI requires human ingenuity, expertise, and data-driven methodologies
- How is Generative AI redefining roles and reshaping the workforce
- The rise of Generative AI: Creating new roles and addressing the skills gap
- Bridging the AI skills gap with upskilling
What do people think about Generative AI?
Generative AI has gained considerable attention in emerging technologies and sparked curiosity among experts and the public. However, a disparity often exists between what people perceive Generative AI to be and what it truly represents.
At first glance, people might envision Generative AI as a mystical force capable of creating sentient beings or generating groundbreaking discoveries with minimal human intervention. It’s as if they imagine a magical box that can conjure innovative ideas and artworks or even compose symphonies at the touch of a button. Speculation and misinformation can fuel these fantastical perceptions, leading to unrealistic expectations of what Generative AI can actually achieve.
What is Generative AI really?
In reality, Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating and generating new content, whether it’s images, music, text, or other forms of data. It involves training machine learning models to learn from existing examples and generate new outputs that resemble the learned patterns. Rather than being a magical box, Generative AI is a set of algorithms and techniques that rely on vast amounts of data, complex mathematical models, and computational power.
Generative AI is not a completely autonomous entity capable of independent thought or creativity. It lacks the intuitive understanding and consciousness that humans possess. Instead, it functions as a powerful tool that augments human creativity and problem-solving abilities. It can assist artists, designers, researchers, and professionals in various domains by generating novel ideas, providing inspiration, and automating repetitive tasks.
For example, a visual artist may employ Generative AI to generate various designs, patterns, or even entire scenes, which they can refine and incorporate into their artwork. Similarly, a music composer can leverage Generative AI to explore different melodies, harmonies, and arrangements, sparking new ideas and enhancing their creative process.
Generative AI requires human ingenuity, expertise, and data-driven methodologies
Generative AI requires skilled practitioners who understand its underlying principles, possess programming and machine learning knowledge, and have the ability to fine-tune and guide the generated outputs. It is a collaborative partnership between humans and machines, where human expertise provides guidance and contextual understanding while AI algorithms generate possibilities and explore uncharted territories.
As people become more informed about Generative AI, bridging the gap between perception and reality is essential. By demystifying its capabilities and highlighting its potential applications, we can better understand Generative AI as a powerful tool for augmenting human creativity, problem-solving, and productivity. With this knowledge, we can embrace its possibilities and explore how to upskill in Generative AI can shape the future of various industries and domains.
How is Generative AI redefining roles and reshaping the workforce
By leveraging Generative AI, customer support agents experienced an impressive 14 percent increase in efficiency. Notably, even the least skilled and least experienced workers saw substantial improvements, with productivity skyrocketing by an astounding 35 percent.
Goldman Sachs’ recent report presents a staggering finding that the potential of generative AI to elevate global GDP by an impressive 7 percent.
According to Pitchbook, the Generative AI market will surge at 32.2% CAGR, reaching $98.1B by 2026.
As the capabilities of Generative AI continue to evolve, professionals and organizations should navigate this shifting terrain to harness its potential while adapting to the changing demands of the workforcehttps://hrforecast.com/key-labor-market-insights-for-this-year/. In this era of creative disruption, the interplay between generative AI and the roles it affects becomes a captivating symphony of adaptation, upskilling, and reimagining possibilities. Let us explore the impact of generative AI on different roles and the journey ahead for individuals and industries alike.
Generative AI is poised to impact various roles across different industries significantly. Here are some key uses cases wherein certain roles will be affected and examples of roles that will experience changes:
Automation of repetitive tasks. Generative AI can automate repetitive and mundane tasks, leading to changes in roles that involve manual or rule-based work. For example, Generative AI can help data entry clerks automate tasks, reducing the need for manual data input.
Optimization and decision support. Generative AI can assist in optimizing processes and providing decision support, impacting roles that involve data analysis and decision-making. For example, AI algorithms can assist financial analysts in analyzing financial data and generating insights, supporting financial decision-making processes.
Creative assistance and content creation. Generative AI can aid in creative tasks and content generation, influencing roles that involve artistic or creative work. For example, graphic designers can use AI-powered tools to generate design suggestions and layouts, or even assist in creating graphics and visual elements.
Quality assurance and ethical oversight. Generative AI may impact roles in ensuring AI systems’ accuracy, fairness, and ethical use. For example, AI auditors can verify the accuracy and fairness of AI-generated outputs and assess compliance with regulations and guidelines.
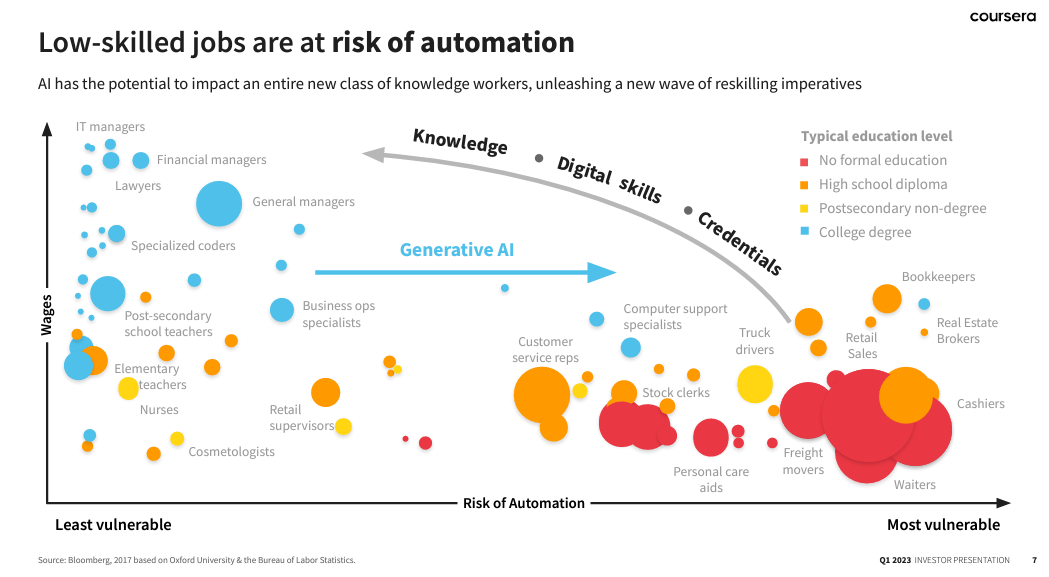
While generative AI may affect certain aspects of these roles, it also presents opportunities for professionals to adapt, upskill, and leverage AI technology to enhance their work and create new value. Take a look at the impact of generative AI on roles depending on the specific industry, organization, and level of integration of AI technologies.
Source: Bloomberg
The rise of Generative AI: Creating new roles and addressing the skills gap
The growing demand for Generative AI is driven by its transformative impact on various industries and the emergence of new roles and opportunities. As Generative AI continues to evolve, organizations recognize its potential and seek professionals with the right skills to harness its capabilities. Here’s an elaboration on the demand for Generative AI and the skills needed:
Creation of new roles
Generative AI has given rise to novel job positions unheard of until recently. Roles like prompt engineers and AI trainers have emerged to facilitate the training and optimization of AI models. These positions require individuals who can compose effective text strings and deliver precise results, regardless of background. Such roles are not limited to IT companies but are also applicable in law firms, customer support, publishing companies, and other sectors seeking automation solutions.
Assurance of accuracy and ethics
With the increased reliance on AI, there is a demand for roles such as AI auditors and AI ethicists. AI auditors ensure that the outputs generated by AI systems are accurate, unbiased, and comply with regulations. AI ethicists focus on the ethical use of generative AI, ensuring its responsible implementation and minimizing potential risks.
Technical roles
Alongside the aforementioned roles, technical positions like machine managers are emerging as essential components of the generative AI ecosystem. Machine managers are vital in overseeing AI-operated hardware and systems, enabling effective collaboration between machines and AI instructions.
Impact on job landscape
Generative AI is expected to bring about significant changes in the labor market. While some fear job displacement, historical evidence suggests that new jobs are often created alongside automation. A World Economic Forum report states that 97 million new jobs will be created by 2025 due to AI. However, it is essential to address the AI skills shortage and reskill workers to adapt to the changing landscape.
Bridging the AI skills gap with upskilling
A new survey by Salesforce of more than 500 senior IT leaders revealed that a majority (67%) prioritize generative AI for their business within the next 18 months, with one-third (33%) naming it as a top priority.
The demand for generative AI skills is outpacing the available talent pool. To bridge the skills gap, organizations should implement upskilling and reskilling programs to teach employees about new technologies and skills required to work with generative AI and address the AI skills shortage.
By embracing upskilling initiatives, individuals can acquire the skills needed to thrive in the age of generative AI, ensuring a resilient and adaptable workforce. Contact us to learn how we offer a collaborative approach to help your workforce harness the power of AI, unlock the full potential of generative AI, and shape a future where technology augments human capabilities to achieve remarkable feats.
Stay up to date with our newsletter
Every month, we’ll send you a curated newsletter with our updates and the latest industry news.






















 info@hrforecast.de
info@hrforecast.de
 +49 89 215384810
+49 89 215384810






