Human beings have been fascinated and motivated by problem-solving for as long as time. Let’s start with the classic ancient legend of Oedipus. The Sphinx aggressively addressed anyone who dared to enter Thebes by posing a riddle. If the traveler failed to answer the riddle correctly, the result was death. However, the Sphinx would be destroyed when the answer was finally correct.
Alas, along came Oedipus. He answered correctly. He unlocked this complex riddle and killed the Sphinx.
However, rationality was hardly defined at that time. Today, though, most people assume that it simply takes raw intelligence to be a great problem solver. However, it’s not the only crucial element.
Introduction to key problem-solving skills
You’ve surely noticed that many of the skills listed in the problem-solving process are repeated. This is because having these abilities and talents are so crucial to the entire course of getting a problem solved. Let’s look at some key problem-solving skills that are essential in the workplace.
Communication, listening, and customer service skills
In all the stages of problem-solving, you need to listen and engage to understand what the problem is and come to a conclusion as to what the solution may be. Another challenge is being able to communicate effectively so that people understand what you’re saying. It further rolls into interpersonal communication and customer service skills, which really are all about listening and responding appropriately.
Data analysis, research, and topic understanding skills
To produce the best solutions, employees must be able to understand the problem thoroughly. This is possible when the workforce studies the topic and the process correctly. In the workplace, this knowledge comes from years of relevant experience.
Dependability, believability, trustworthiness, and follow-through
To make change happen and take the following steps towards problem-solving, the qualities of dependability, trustworthiness, and diligence are a must. For example, if a person is known for not keeping their word, laziness, and committing blunders, that is not someone you’ll depend on when they provide you with a solution, will you?
Leadership, team-building, and decision-making
A true leader can learn and grow from the problems that arise in their jobs and utilize each challenge to hone their leadership skills. Problem-solving is an important skill for leaders who want to eliminate challenges that can otherwise hinder their people’s or their business’ growth. Let’s take a look at some statistics that prove just how important these skills are:
A Harvard Business Review study states that of all the skills that influence a leader’s success, problem-solving ranked third out of 16.
According to a survey by Goremotely.net, only 10% of CEOs are leaders who guide staff by example.
Another study at Havard Business Review found a direct link between teambuilding as a social activity and employee motivation.
Are you looking for a holistic way to develop leaders in your workplace?
Numerous skills and attributes define a successful one from a rookie when it comes to leaders. Our leadership development plan (with examples!) can help HR leaders identify potential leaders that are in sync with your company’s future goals.
Why is problem solving important in the workplace?
As a business leader, when too much of your time is spent managing escalations, the lack of problem-solving skills may hurt your business. While you may be hiring talented and capable employees and paying them well, it is only when you harness their full potential and translate that into business value that it is considered a successful hire.
The impact of continuing with poor problem-solving skills may show up in your organization as operational inefficiencies that may also manifest in product quality issues, defects, re-work and non-conformance to design specifications. When the product is defective, or the service is not up to the mark, it directly affects your customer’s experience and consequently reflects on the company’s profile.
At times, poor problem-solving skills could lead to missed market opportunities, slow time to market, customer dissatisfaction, regulatory compliance issues, and declining employee morale.
Problem-solving skills are important for individual business leaders as well. Suppose you’re busy responding to frequent incidents that have the same variables. In that case, this prevents you from focusing your time and effort on improving the future success of business outcomes.
Proven methods to assess and improve problem-solving skills
Pre-employment problem-solving skill assessment
Recent research indicates that up to 85% of resumes contain misleading statements. Similarly, interviews are subjective and ultimately serve as poor predictors of job performance.
To provide a reliable and objective means of gathering job-related information on candidates, you must validate and develop pre-employment problem-solving assessments. You can further use the data from pre-employment tests to make informed and defensible hiring decisions.
Depending on the job profile, below are examples of pre-employment problem-solving assessment tests:
Personality tests: The rise of personality testing in the 20th century was an endeavor to maximize employee potential. Personality tests help to identify workplace patterns, relevant characteristics, and traits, and to assess how people may respond to different situations.
Examples of personality tests include the Big five personality traits test and Mercer | Mettl’s Dark Personality Inventory.
Cognitive ability test: A pre-employment aptitude test assesses individuals’ abilities such as critical thinking, verbal reasoning, numerical ability, problem-solving, decision-making, etc., which are indicators of a person’s intelligence quotient (IQ). The test results provide data about on-the-job performance. It also assesses current and potential employees for different job levels.
Criteria Cognitive Aptitude test, McQuaig Mental Agility Test, and Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory are commonly used cognitive ability assessment tests.
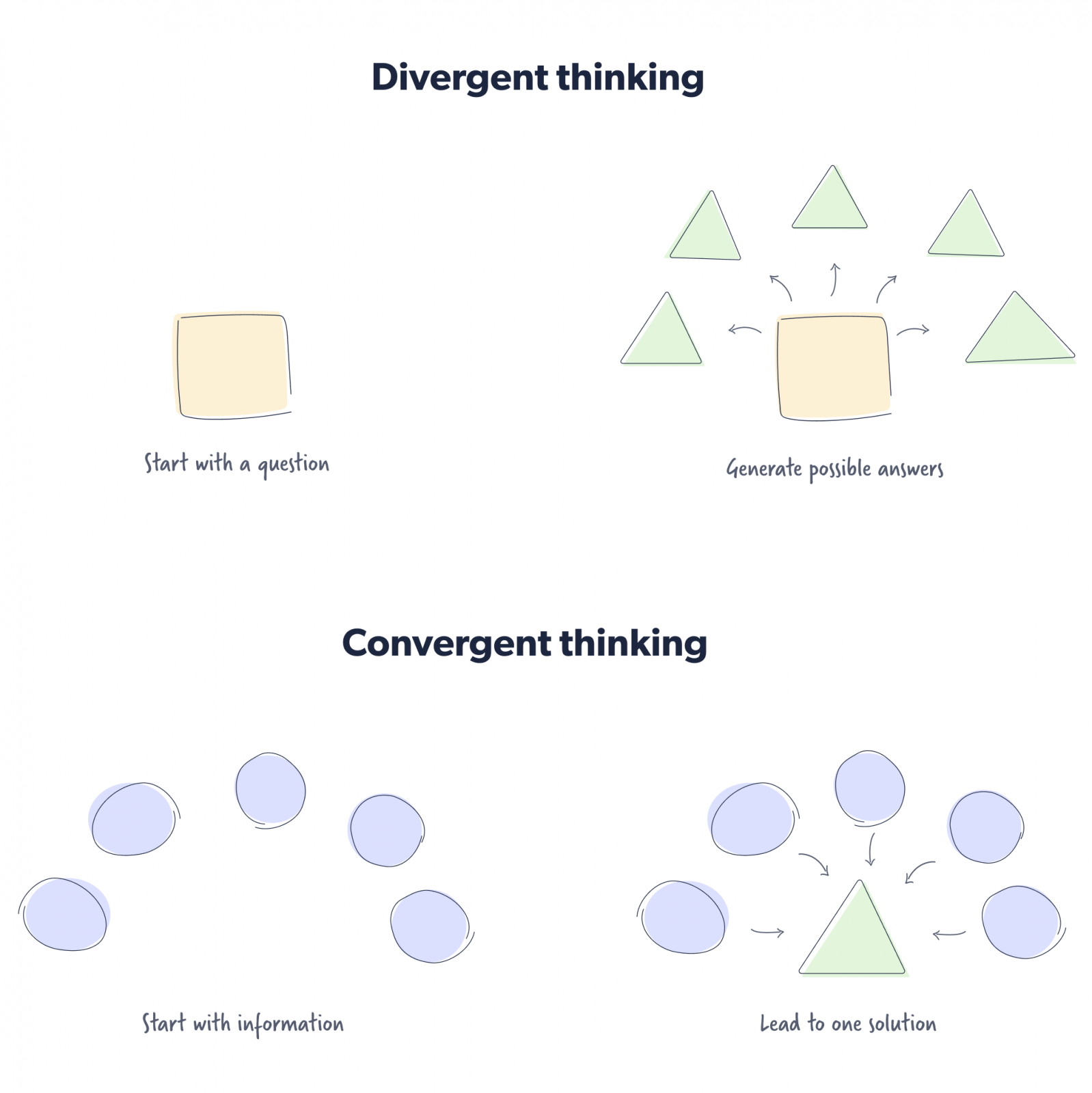
Convergent and divergent thinking methods
American psychologist JP Guilford coined the terms “convergent thinking” and “divergent thinking” in the 1950s.
Convergent thinking involves starting with pieces of information and then converging around a solution. An example would be determining the correct answer to a multiple-choice question.
The nature of the question does not demand creativity but rather inherently encourages a person to consider the veracity of each answer provided before selecting the single correct one.
Divergent thinking, on the other hand, starts with a prompt that encourages people to think critically, diverging towards distinct answers. An example of divergent thinking would be asking open-ended questions.
Here’s an example of what convergent thinking and a divergent problem-solving model would look like.
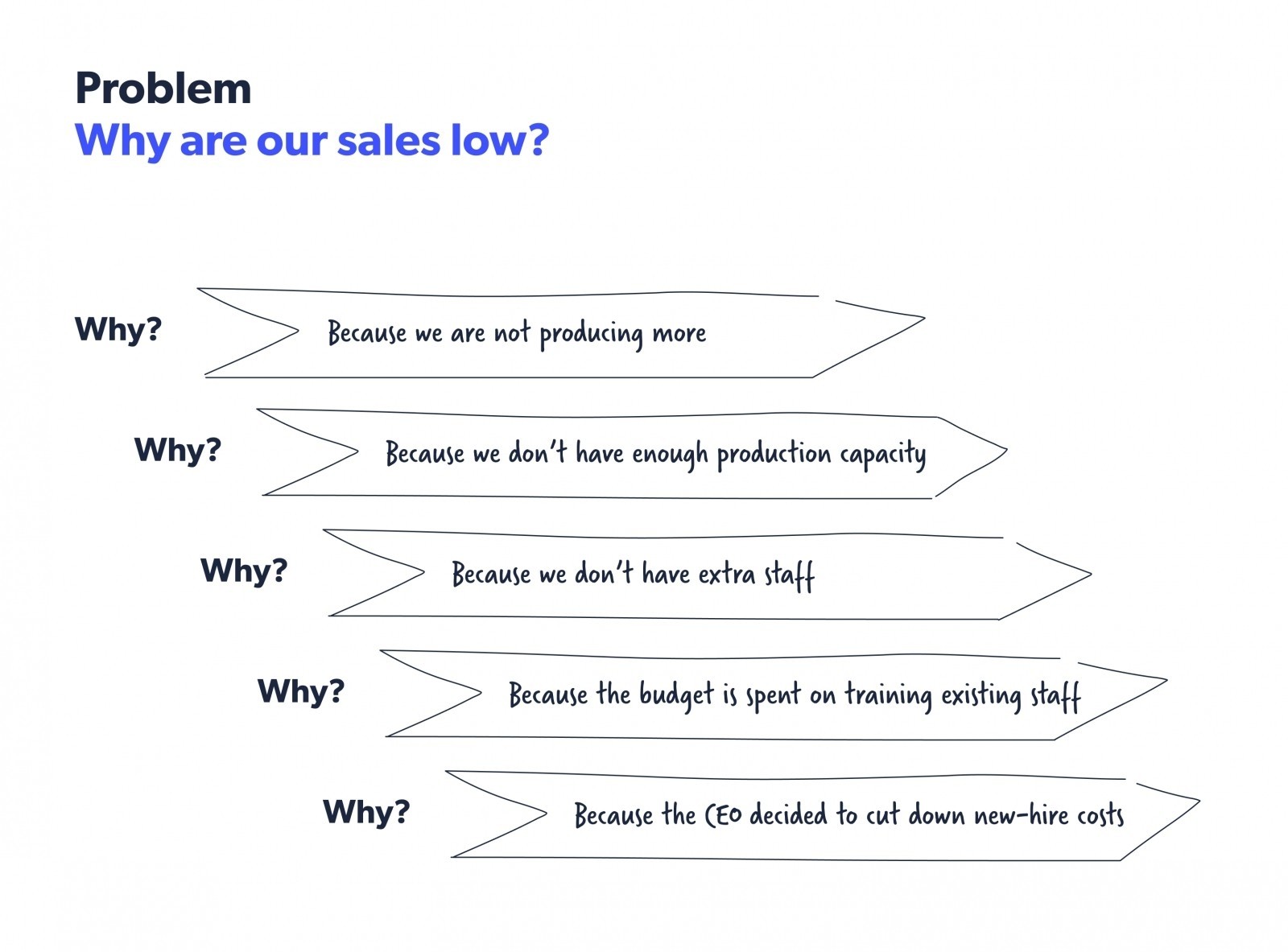
5 whys
The 5 whys method, developed by Sakichi Toyoda, is part of the Toyota production system. In this method, when you come across a problem, you analyze the root cause by asking “Why?” five times. By recognizing the countermeasure, you can prevent the problem from recurring. Here’s an example of the 5 whys method.
Source: Kanbanzie
This method is specifically useful when you have a recurring problem that reoccurs despite repeated actions to address it. It indicates that you are treating the symptoms of the problem and not the actual problem itself.
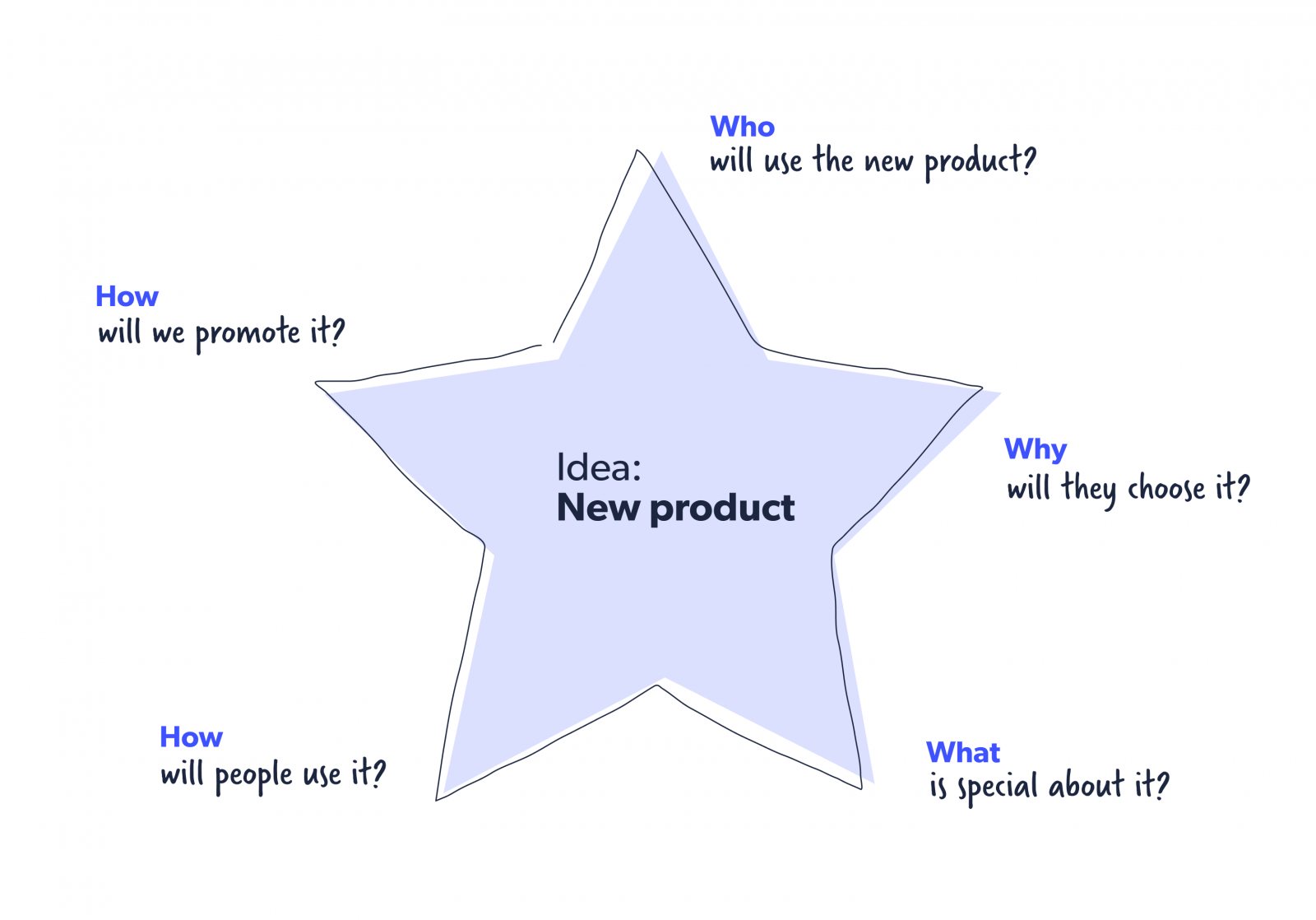
Starbursting
While brainstorming is about the team coming together to try to find answers, starbursting flips it over and asks everyone to think of questions instead. Here’s an example of the starbursting method.
The idea of this method is to go and expand from here, layering more and more questions until you’ve covered every eventuality of the problem.
Use of data analysis to measure improvement in problem-solving skills for your organization
Problem-solving and data analytics are often used together. Supporting data is very handy whenever a particular problem occurs. By using data analytics, you can find the supporting data and analyze it to use for solving a specific problem.
However, we must emphasize that the data you’re using to solve the problem is accurate and complete. Otherwise, misleading data may take you off track of the problem at hand or even make it appear more complex than it is. Moreover, as you gain knowledge about the current problem, it further eases the way to solve it.
Let’s dig deeper into the top 3 reasons data analytics is important in problem-solving.
1. Uncover hidden details
Modern data analytics tools have numerous features that let you analyze the given data thoroughly and find hidden or repeating trends without needing any extra human effort. These automated tools are great at extracting the depths of data, going back way into the past.
2. Automated models
Automation is the future. Businesses don’t have enough time or the budget to encourage manual workforces to go through loads of data to solve business problems. Instead, the tools can collect, combine, clean, and transform the relevant data all by themselves and finally use it to predict the solutions.
3. Explore similar problems
When you use a data analytics approach to solve problems, you can collect all the data available and store it. It can assist you when you find yourself in similar problems, providing references for how such issues were tackled in the past.
If you’re looking for ways to help develop problem-solving skills in the workplace and want to build a team of employees who can solve their own problems, contact us to learn how we can help you achieve it.
Stay up to date with our newsletter
Every month, we’ll send you a curated newsletter with our updates and the latest industry news.
























 info@hrforecast.de
info@hrforecast.de
 +49 89 215384810
+49 89 215384810






